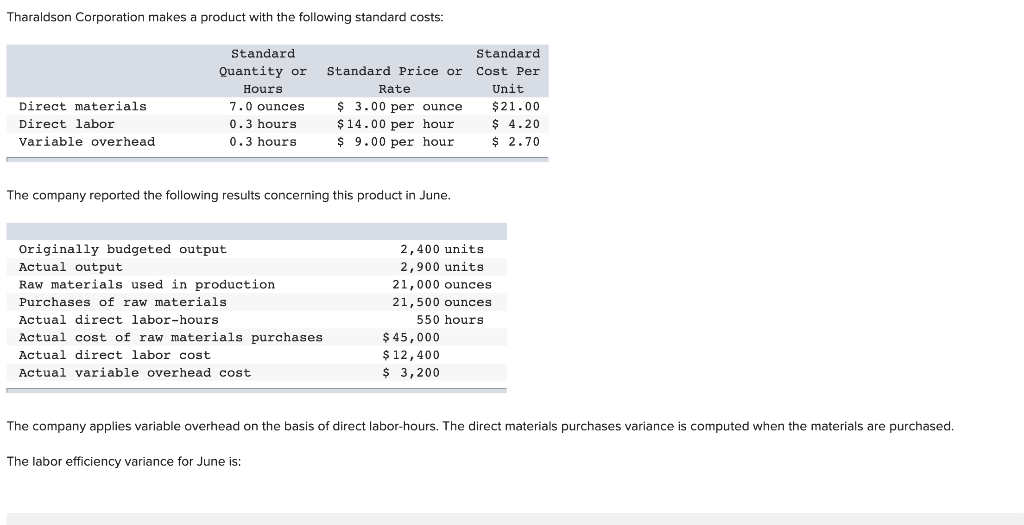
The direct materials variances for NoTuggins are presented in Exhibit 8-4. Refer to the total direct materials variance in the top section of the template. Total standard quantity is calculated as standard quantity per unit times actual production or 4.2 feet of flat nylon cord per unit times 150,000 units produced equals 630,000 feet of flat nylon cord.
Total variable manufacturing costs variance
Brad invented NoTuggins, a revolutionary dog harness that stops dogs from pulling when connected to a leash by humanely redistributing the dog’s pulling force. NoTuggins was featured as the most innovative new harness by the International Kennel Association. Although the product was selling well, product costs were higher than expected, translating into lower profits. Brad decided to conduct a standard costs variance analysis to see if he could isolate the issue, or issues. The standard costs to make one unit of NoTuggins and the actual production costs data for the period are presented in Exhibit 8-1 below. You are deciding whether to purchase a pizza franchise or open your own restaurant specializing in pizza.
Direct Materials Quantity Variance
- But note that while production facility electricity costs are treated as overhead, the organization’s administrative facility electrical costs are not included as overhead costs.
- For each cost, identify its origination in a job order costing environment.
- Some examples of direct materials for different industries are shown in Table 4.2.
- The training company may charge for the hours worked by instructors in preparation and delivery of the course, plus a fee for the course materials.
Refer to the total direct labor variance in the top section of the template. Total standard quantity is calculated as standard quantity per unit times actual production or 0.25 direct labor hours per unit times 150,000 actual quantity is the actual direct material or direct labor used to manufacture the units produced equals 37,500 direct labor hours. Total direct labor costs per the standard amounts allowed are calculated as total standard quantity (37,500) times standard rate per hour ($18) equals $675,000.
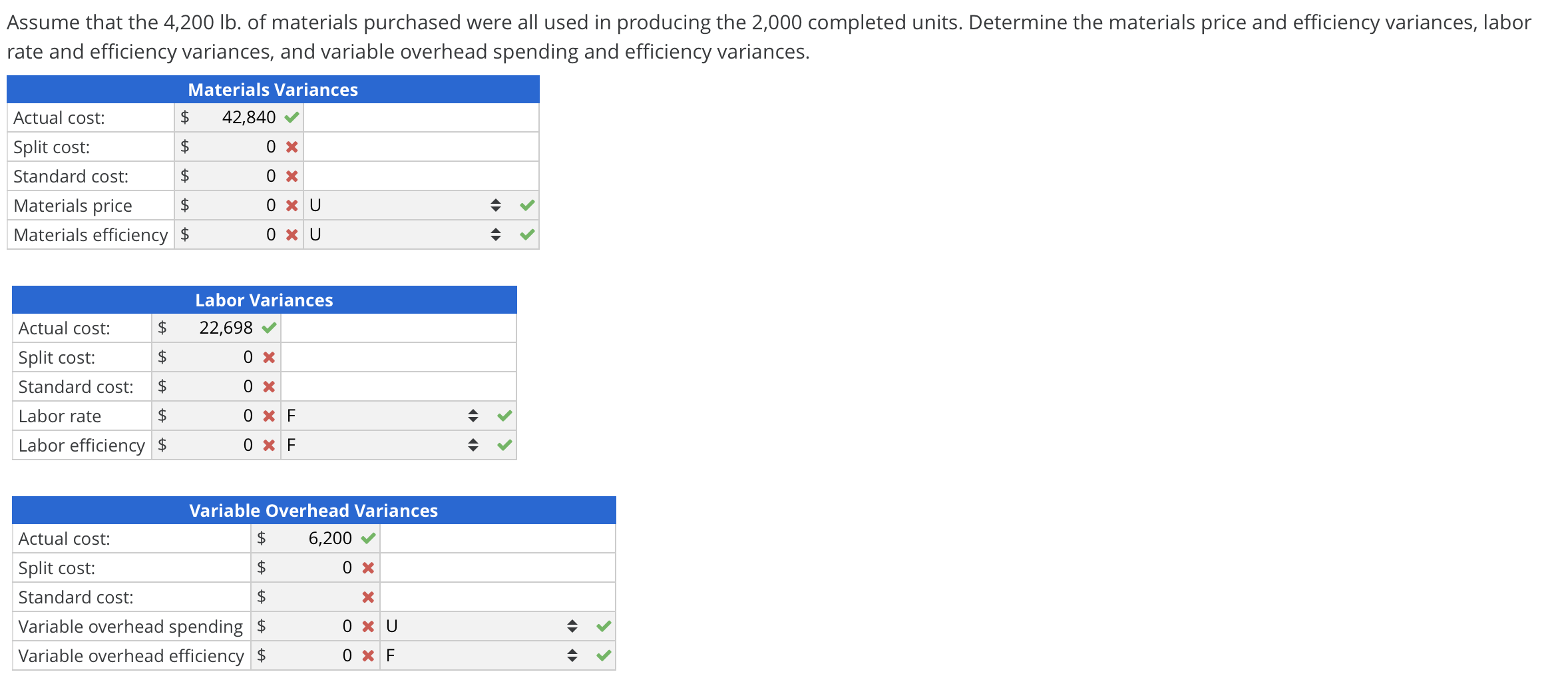
Standard costs variance template
Standard costs are cost targets used to make financial projections and evaluate performance. A cost formula is used to predict the expected cost for a specific expenditure. Homework questions can be used for additional practice or can be assigned in an academic setting. Homework questions can be assigned, with auto-grading and export, to specific learning management platforms, e.g., Canvas, Blackboard, etc.
Video Illustration 8-4: Computing variable manufacturing overhead variances
Using the standard and actual data given for Lastlock and the direct materials variance template, compute the direct materials variances. Determine whether a variance is favorable or unfavorable by reliance on reason or logic. If more materials were used than the standard quantity, or if a price greater than the standard price was paid, the variance is unfavorable. An unfavorable outcome means the actual costs related to materials were more than the expected (standard) costs. If the outcome is a favorable outcome, this means the actual costs related to materials are less than the expected (standard) costs.
A template to compute the standard cost variances related to direct material, direct labor, and variable manufacturing overhead is presented in Exhibit 8-11. The completed top section of the template contains all the numbers needed to compute the variable manufacturing overhead efficiency (quantity) and rate (price) variances. The variable manufacturing overhead efficiency and rate variances are used to determine if the overall variance is an efficiency issue, rate issue, or both. A template to compute the total variable manufacturing overhead variance, variable manufacturing overhead efficiency variance, and variable manufacturing overhead rate variance is provided in Exhibit 8-9. Standard costs are established for all direct labor used in the manufacturing process.
A cost driver is a production factor that causes a company to incur costs. An example would be a bakery that produces a line of apple pies that it markets to local restaurants. To make the pies requires that the bakery incur labor costs, so it is safe to say that pie production is a cost driver. It should also be safe to assume that the more pies made, the greater the number of labor hours experienced (also assuming that direct labor has not been replaced with a greater amount of automation). We assume, in this case, that one of the marketing advantages that the bakery advertises is 100% handmade pastries.
List the expenses necessary to sell pizza and identify them as a fixed cost or variable cost; as a manufacturing cost or sales and administrative costs; and as a direct materials, direct labor, or overhead. For each overhead item, state whether it is an indirect material expense, indirect labor expense, or other. For each cost, identify its origination in a job order costing environment. Direct labor is the total cost of wages, payroll taxes, payroll benefits, and similar expenses for the individuals who work directly on manufacturing a particular product.
The journal entries to reflect the flow of costs from raw materials to work in process to finished goods are provided in the section describing how to Prepare Journal Entries for a Job Order Cost System. Returning to the example of Dinosaur Vinyl’s order for Macs & Cheese’s stadium sign, Figure 4.7 shows the materials requisition form for Job MAC001. This form indicates the quantity and specific items to be put into the work in process. It also transfers the cost of those items to the work in process inventory and decreases the raw materials inventory by the same amount. The raw materials inventory department maintains a copy to document the change in inventory levels, and the accounting department maintains a copy to properly assign the costs to the particular job. Connie’s Candy paid $2.00 per pound more for materials than expected and used 0.25 pounds more of materials than expected to make one box of candy.
